This example demonstrates how to use XAF's Security System to implement the following access control/authorization requirements:
- User Role (users: user1, user12, user2, user22) - read-only access to their own Department, corresponding Department Goals, the User list in that department, and Tasks assigned to these users.
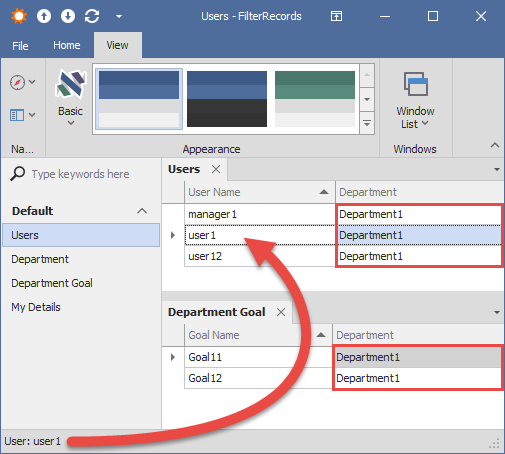
- Manager Role (users: manager1, manager2) - read-write access to their own Department, corresponding Department Goals, User list, and their Tasks. Managers can link or unlink existing entities.
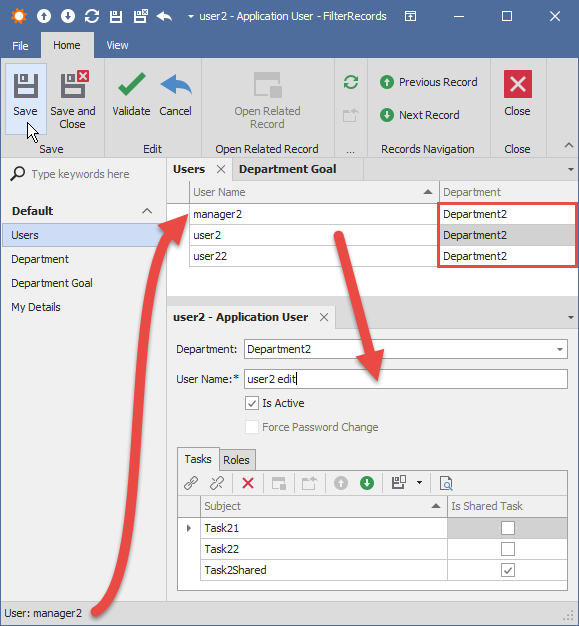
- Administrator Role (users: Admin) - full access to all entities in the application. Administrators can create new entities.
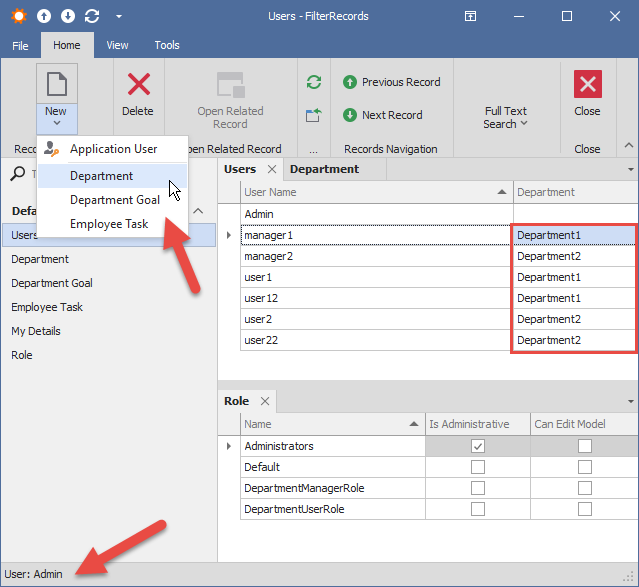
- All users can view shared Tasks. All managers can edit shared Tasks.
You can log in as any user. Type in a user name and an empty password.
Implementation Details
- In the SolutionName.Module/DatabaseUpdate/Updater file, configure security permissions at the type, object, and member level (with criteria). To build complex criteria against associated objects, use the ContainsOperator together with the built-in
CurrentUserIdandIsCurrentUserInRolecriteria functions. - In the SolutionName.Module/BusinessObjects folder, implement the
Department,DepartmentGoal, andMyTaskbusiness classes. - Set the following settings in the
builder.Security.UseIntegratedMode()method call:options.Events.OnSecurityStrategyCreated = securityStrategy => { ((SecurityStrategy)securityStrategy).AssociationPermissionsMode = AssociationPermissionsMode.Manual; }; options.RoleType = typeof(PermissionPolicyRole); options.UserType = typeof(FilterRecords.Module.BusinessObjects.ApplicationUser); options.UserLoginInfoType = typeof(FilterRecords.Module.BusinessObjects.ApplicationUserLoginInfo); - In the SolutionName.Module/Controllers folder, optionally implement a Controller to hide the protected content columns in a List View and Property Editors in a Detail View. For more information, see this help topic.
NOTE: You can find implementation details for the XPO ORM in the 18.2.2+ branch.
More Examples
Does this example address your development requirements/objectives?
(you will be redirected to DevExpress.com to submit your response)
Example Code
C#using System.Configuration;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.ApplicationBuilder;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Win.ApplicationBuilder;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Win;
using DevExpress.Persistent.Base;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.EFCore;
using DevExpress.EntityFrameworkCore.Security;
using DevExpress.XtraEditors;
using DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.PermissionPolicy;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Design;
namespace FilterRecords.Win;
public class ApplicationBuilder : IDesignTimeApplicationFactory {
public static WinApplication BuildApplication(string connectionString) {
var builder = WinApplication.CreateBuilder();
builder.UseApplication<FilterRecordsWindowsFormsApplication>();
builder.Modules
.AddConditionalAppearance()
.AddValidation(options => {
options.AllowValidationDetailsAccess = false;
})
.Add<FilterRecords.Module.FilterRecordsModule>()
.Add<FilterRecordsWinModule>();
builder.ObjectSpaceProviders
.AddSecuredEFCore().WithDbContext<FilterRecords.Module.BusinessObjects.FilterRecordsEFCoreDbContext>((application, options) => {
// Uncomment this code to use an in-memory database. This database is recreated each time the server starts. With the in-memory database, you don't need to make a migration when the data model is changed.
// Do not use this code in production environment to avoid data loss.
// We recommend that you refer to the following help topic before you use an in-memory database: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/ef/core/testing/in-memory
//options.UseInMemoryDatabase("InMemory");
options.UseSqlServer(connectionString);
options.UseChangeTrackingProxies();
options.UseObjectSpaceLinkProxies();
})
.AddNonPersistent();
builder.Security
.UseIntegratedMode(options => {
options.RoleType = typeof(PermissionPolicyRole);
options.UserType = typeof(FilterRecords.Module.BusinessObjects.ApplicationUser);
options.UserLoginInfoType = typeof(FilterRecords.Module.BusinessObjects.ApplicationUserLoginInfo);
options.Events.OnSecurityStrategyCreated = securityStrategy => {
((SecurityStrategy)securityStrategy).AssociationPermissionsMode = AssociationPermissionsMode.Manual;
};
})
.UsePasswordAuthentication();
builder.AddBuildStep(application => {
application.ConnectionString = connectionString;
#if DEBUG
if(System.Diagnostics.Debugger.IsAttached && application.CheckCompatibilityType == CheckCompatibilityType.DatabaseSchema) {
application.DatabaseUpdateMode = DatabaseUpdateMode.UpdateDatabaseAlways;
}
#endif
});
var winApplication = builder.Build();
return winApplication;
}
XafApplication IDesignTimeApplicationFactory.Create()
=> BuildApplication(XafApplication.DesignTimeConnectionString);
}
C#using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Security;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.ApplicationBuilder;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Blazor.ApplicationBuilder;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Blazor.Services;
using DevExpress.Persistent.Base;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Cookies;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Server.Circuits;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using FilterRecords.Blazor.Server.Services;
using DevExpress.Persistent.BaseImpl.EF.PermissionPolicy;
using DevExpress.ExpressApp.Core;
using FilterRecords.Module.BusinessObjects;
namespace FilterRecords.Blazor.Server;
public class Startup {
public Startup(IConfiguration configuration) {
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
// For more information on how to configure your application, visit https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=398940
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {
services.AddSingleton(typeof(Microsoft.AspNetCore.SignalR.HubConnectionHandler<>), typeof(ProxyHubConnectionHandler<>));
services.AddRazorPages();
services.AddServerSideBlazor();
services.AddHttpContextAccessor();
services.AddScoped<CircuitHandler, CircuitHandlerProxy>();
services.AddXaf(Configuration, builder => {
builder.UseApplication<FilterRecordsBlazorApplication>();
builder.Modules
.AddConditionalAppearance()
.AddValidation(options => {
options.AllowValidationDetailsAccess = false;
})
.Add<FilterRecords.Module.FilterRecordsModule>()
.Add<FilterRecordsBlazorModule>();
builder.ObjectSpaceProviders
.AddSecuredEFCore().WithDbContext<FilterRecords.Module.BusinessObjects.FilterRecordsEFCoreDbContext>((serviceProvider, options) => {
// Uncomment this code to use an in-memory database. This database is recreated each time the server starts. With the in-memory database, you don't need to make a migration when the data model is changed.
// Do not use this code in production environment to avoid data loss.
// We recommend that you refer to the following help topic before you use an in-memory database: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/ef/core/testing/in-memory
//options.UseInMemoryDatabase("InMemory");
string connectionString = null;
if(Configuration.GetConnectionString("ConnectionString") != null) {
connectionString = Configuration.GetConnectionString("ConnectionString");
}
#if EASYTEST
if(Configuration.GetConnectionString("EasyTestConnectionString") != null) {
connectionString = Configuration.GetConnectionString("EasyTestConnectionString");
}
#endif
ArgumentNullException.ThrowIfNull(connectionString);
options.UseSqlServer(connectionString);
options.UseXafServiceProviderContainer(serviceProvider);
options.UseLazyLoadingProxies();
options.UseChangeTrackingProxies();
options.UseObjectSpaceLinkProxies();
})
.AddNonPersistent();
builder.Security
.UseIntegratedMode(options => {
options.Events.OnSecurityStrategyCreated = securityStrategy => {
((SecurityStrategy)securityStrategy).AssociationPermissionsMode = AssociationPermissionsMode.Manual;
};
options.RoleType = typeof(PermissionPolicyRole);
// ApplicationUser descends from PermissionPolicyUser and supports the OAuth authentication. For more information, refer to the following topic: https://docs.devexpress.com/eXpressAppFramework/402197
// If your application uses PermissionPolicyUser or a custom user type, set the UserType property as follows:
options.UserType = typeof(FilterRecords.Module.BusinessObjects.ApplicationUser);
// ApplicationUserLoginInfo is only necessary for applications that use the ApplicationUser user type.
// If you use PermissionPolicyUser or a custom user type, comment out the following line:
options.UserLoginInfoType = typeof(FilterRecords.Module.BusinessObjects.ApplicationUserLoginInfo);
})
.AddPasswordAuthentication(options => {
options.IsSupportChangePassword = true;
});
});
services.AddAuthentication(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme).AddCookie(options => {
options.LoginPath = "/LoginPage";
});
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) {
if(env.IsDevelopment()) {
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
using(var scope = app.ApplicationServices.CreateScope()) {
// var dbContextFactory = dbContextBuilder.GetDbContextFactory(serviceProvider);
var factory = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IDbContextFactory<FilterRecordsEFCoreDbContext>>();
using(var context = factory.CreateDbContext()) {
context.Database.EnsureDeleted();
context.Database.EnsureCreated();
}
}
}
else {
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
// The default HSTS value is 30 days. To change this for production scenarios, see: https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseRequestLocalization();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseXaf();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => {
endpoints.MapXafEndpoints();
endpoints.MapBlazorHub();
endpoints.MapFallbackToPage("/_Host");
endpoints.MapControllers();
});
}
}